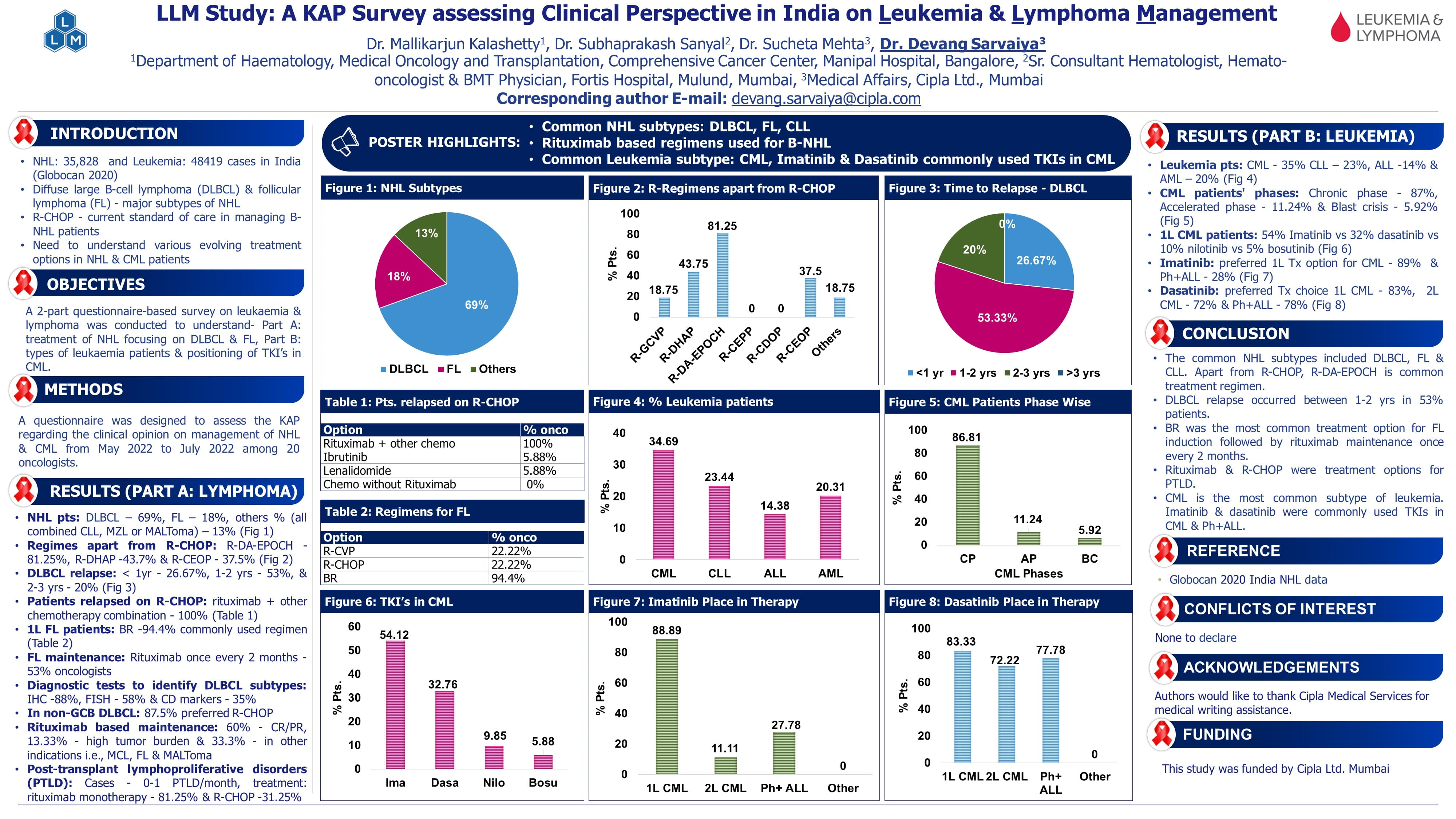
Indian Experience: Impact of Rituximab Maintenance (RM) on Outcomes in Follicular Lymphoma (FL)
- Retrospective study included 95 FL patients with Ann Arbor Staging III/IV 86% patients receiving RM (n = 44) for every 2 months for 2 years
- FLIPI Index: 13 (14%) were low risk, 23 (24%) intermediate risk, and 59 (62%) were high risk.
- ORR: 89%, CR: 71%, during follow-up 28% patients experienced relapses and 10 transformed to DLBCL.
- At the median follow-up of 60 months, median OS was NR, median PFS was 114 months.
- Estimated 5.0-year PFS were 89.0% vs 61.0% respectively in the maintenance vs non-maintenance group.
- Rituximab maintenance therapy was significantly associated with better OS & PFS (aHR = 0.05, 95% CI 0.01-0.37, p=0.004) & (aHR = 0.28, 95% CI 0.11-0.68, p=0.005) respectively.
- This study is the first from India to demonstrate that RM after induction immunochemotherapy significantly improves both PFS and OS in FL.
Reference
Harish Pant Jr et al, Impact of rituximab maintenance on outcomes in follicular lymphoma: An Indian experience. JCO 43, e19044, (2025).
Effectiveness of Rituximab plus Chemotherapy (R-chemo) in Pediatric Burkitt Lymphoma
- Systematic review included 1280 patients from 5 clinical trials with 5-18 age group patients.
- R+chemo demonstrated improved efficacy, with a higher OS rate (HR 0.52; 95% CI 0.11-0.93; p < 0.01) and EFS with (HR = 0.50; 95% CI 0.21-0.79; p < 0.01) against control.
- Toxic events, secondary cancer and relapses or progression outcomes were not statistically significant between two arms.
- This review suggests that R + chemo is an effective treatment approach for Burkitt lymphoma in children and adolescents.
Reference
Cainã Rodrigues, Effectiveness of rituximab plus chemotherapy in pediatric Burkitt lymphoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JCO 43, e22006, (2025).
Phase III VERIFY: Rusfertide (RUS) vs Placebo (PBO) for Polycythemia Vera (PV)
- During Wks 20-32, significantly more pts in the RUS (76.9%) achieved a clinical response vs PBO in phlebetomy (PHL)-dependent PV (32.9%) (p<0.0001).
- More pts treated with RUS maintained Hct <45% from Wks 0-32 vs PBO (RUS, 62.6%; PBO, 14.4%; p<0.0001).
- Pts treated with RUS demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in the PROMIS Fatigue SF-8a total T-score and MFSAF TSS.
- AE (RUS vs PBO): injection site reactions (55.9% and 32.9%), anemia (15.9% and 4.1%), fatigue (15.2% and 15.8%) and serious AE (3.4% vs 4.8%).
- In pts with PV receiving SOC, RUS (targeting hepcidin pathway) resulted in a statistically significant reduction in the mean number of PHLs, improved Hct control and significant improvement in the PROMIS Fatigue SF-8a and MFSAF PROs.
Reference
Andrew Kuykendall, Results from VERIFY, a phase 3, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled study of rusfertide for treatment of polycythemia vera (PV). JCO 43, LBA3, (2025).
Dose-Adjusted Etoposide, Prednisone, Vincristine, Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin (DA-EPOCH) ± Rituximab with Tafasitamab (R + Tafa) for Adults with Newly Diagnosed Philadelphia Chromosome-Negative B Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ND Ph- B-ALL)
- In a phase II trial of DA-EPOCH ± R + Tafa for ND Ph- B-ALL, with 15 evaluable; the median age was 67 years (range: 44-84), and 67% had poor-risk cytogenetics.
- The complete response rate among evaluable patients was 80%; measurable residual disease negativity (MRD-) by multiparameter flow cytometry (MFC) after cycle 1 was 40%, increasing to 71% by cycle 4.
- Among patients who were MRD- by MFC, 56% (5/9) were also MRD- by high-throughput sequencing.
- Initial cerebrospinal fluid evaluations identified disease in 3 patients, with HTS confirming positivity in these and 3 additional cases, totaling 6.
- Adverse events included 2 grade 4 serious AEs (sepsis, intracranial hemorrhage); common grade 3 AEs were fibrinogen decrease (5), infections (5), febrile neutropenia (4), hypotension (3) & syncope (2).
- No relapses occurred during follow-up (0.6-21 months) & 4 patients died, primarily from non-relapse causes.
- In a cohort of ND Ph- B-ALL, the addition of Tafa to DA-EPOCH ± R led to rates of MRD- that are higher than historical rates, with similar toxicity.
Reference
Noam E. Kopmar et al, Initial results from a phase II study of dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin (DA-EPOCH) ± rituximab (R) + tafasitamab (tafa) for adults with newly-diagnosed (ND) Philadelphia chromosome negative (Ph-) B lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). JCO 43, 6540, (2025).
COMMANDS Trial: Survival and Response Duration for Transfusion Independence in Erythropoiesis Stimulating Agent-Naive Patients with Low-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS): Luspatercept (LUSPA) vs Epoetin Alfa (EA).
- Red blood cell transfusion independence (RBC-TI) for ≥12 weeks was achieved by 76.4% of patients in LUSPA group vs 55.8% in EA, with a median cumulative duration of RBC-TI of 187.3 weeks vs 94.9 weeks.
- The median duration of the longest RBC-TI period was significantly longer for LUSPA at 126.6 weeks vs 86.7 weeks for EA (HR = 0.64).
- Median OS was not reached for LUSPA, while it was 46.7 months for EA, with 3-year OS rates of 63.8% and 62.2%; progression to AML was comparable between groups (20.9% vs 26.3%).
- LUSPA led to improvements in response rate and duration, with a positive OS trend requiring further evaluation & signifying a new standard of care for anemia in first-line LR-MDS.
Reference
Guillermo Garcia-Manero et al, Overall survival (OS) and duration of response for transfusion independence (TI) in erythropoiesis stimulating agent (ESA)–naive patients (pts) with very low-, low-, or intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) treated with luspatercept (LUSPA) vs epoetin alfa (EA) in the COMMANDS trial. JCO 43, 6512, (2025).
Glofitamab plus GemOx (Glofit-GemOx) in Relapsed/Refractory DLBCL: 2-Year Follow-Up Results from the STARGLO Trial.
- Glofit-GemOx showed significant OS benefits (median not evaluable vs 13.5 mos for R-GemOx; HR = 0.60).
- PFS was also superior for Glofit-GemOx at 13.8 months vs 3.6 mos for R-GemOx (HR = 0.41).
- CRrate was higher in the Glofit-GemOx group at 58.5% vs. 25.3% for R-GemOx; among patients in CR at end of the treatment, OS & PFS rates one year later were 89.3% & 82.4%.
- Safety profile remained consistent; the most common AE was cytokine release syndrome (Grade 1: 32.0%; Grade 2: 10.5%; Grade 3: 2.3%).
- With 2 yrs follow-up, Glofit-GemOx sustained a clinically meaningful benefit in OS and PFS vs R-GemOx in ASCT-ineligible pts with R/R DLBCL, with most (82%) pts in CR at EOT still in remission.
Reference
Jeremy Abramson et al, Glofitamab plus gemcitabine and oxaliplatin (Glofit-GemOx) in patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): 2-year (yr) follow-up of STARGLO. JCO 43, 7015, (2025).
Efficacy Of Isatuximab, Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide, And Dexamethasone (Isa-Krd) in High-Risk (HR) NDMM: Transplant Eligible (TE) patients in GMMG-CONCEPT Trial
- Isa-KRd regimen achieved a 73.2% MRD-negative rate after consolidation in TE HR NDMM patients, with 86.8% achieving MRD-negativity at any point and 40.6% sustaining it for ≥2 years.
- At median follow-up of 42 months, median PFS was 69.7 months, and median OS was not reached.
- Sustained MRD negativity was strongly associated with improved PFS (HR = 0.16)
- Isa-KRd resulted in unprecedented rates of MRD-neg., sustained MRD-neg. and survival supporting the use of Isa-KRd as a standard-of-care regime in this hard-to-treat population.
Reference
Lisa Leypoldt et al, Isatuximab, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (Isa-KRd) for high-risk (HR) newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM): First-time report of the full cohort of transplant-eligible (TE) patients in the GMMG-CONCEPT trial. JCO43, 7509, (2025).
Daratumumab plus bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (DVRd) vs. VRd in Transplant Ineligible (TIE) NDMM: Phase 3 CEPHUS Study
- DVRd significantly increased MRD negativity (60.4% vs 39.3% at 10−5) and ≥ CR rates (80.6% vs. 61.4%) compared to VRd in TIE/early NDMM patients.
- 54-month PFS rate was 69.0% vs. 48.0% in DVRd vs. VRd (HR = 0.51, p=0.0003)
- 5% of DVRd treated patients maintained MRD negativity for ≥12 months, nearly double that of VRd group.
- It showed consistent benefit across subgroups reinforcing the strong efficacy of DVRd in the TIE population.
Reference
Thierry Facon et al, Daratumumab plus bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (DVRd) in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM): Subgroup analysis of transplant-ineligible (TIE) patients in the phase 3 CEPHEUS study. JCO43, 7516, (2025).
IMROZ study phase 3 Results: Isatuximab, bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (Isa-VRd) Beneficial in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma (NDMM)
- Isa-VRd significantly prolonged PFS as compared to VRd in NDMM with 1q21+ (NR vs 39.13 mo; HR = 0.407) or isolated 1q21+ status (NR vs 43.01 mo; HR = 0.369)
- Also, Isa-VRd achieved higher ORR (95.8% vs 85.7%), CR (76.9% vs 60%) and MRD– (63.2% vs 41.4%) for 1q21+.
- Isa-VRd achieved MRD– CR and sustained MRD– for ≥12 months in more patients with 1q21+ (62.1% vs 38.6% & 51.6% vs 22.9%) or isolated 1q21+ status (64.0% vs 36.4% & 50.7% vs 23.6%) vs VRd.
Reference
Dimopoulos M., et al. Isatuximab, bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (Isa-VRd) in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM): Outcomes in patients with 1q21+ status in the phase 3 IMROZ study. JCO 43, 7517, (2025).
An All-Oral Decitabine-Cedazuridine (DEC-C) Plus Venetoclax (VEN) Promising in Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia (ND AML) Ineligible for Intensive Induction Chemotherapy
- As per ELN 2017 classification, response to all-oral regimen of DEC-C was favorable in higher number of patients with ND AML ineligible for intensive induction chemotherapy vs those with adverse response (31.7% vs. 29.7%, respectively).
- DEC-C + VEN oral regimens significantly achieved CR (46.5%) and CRi (63.4%); median time to complete remission was 2.4 months.
- A consistent CR was seen with DEC-C + VEN oral regimens (80.0% of patients at 6 months and 75.3% at 12 months).
- Grade ≥3 TEAR was reported in 98.0% of patients; febrile neutropenia, anemia, and neutropenia being the most common.
- The 30- and 60-day mortality rates were 3.0% and 9.9%, respectively; with the OS being 15.5 months.
- The all-oral regimen of DEC-C plus VEN resulted in comparable safety, response, and survival rates to parenteral AZA plus VEN in pts with newly diagnosed AML ineligible for intensive induction chemotherapy suggesting potential use of DEC-C plus VEN as a treatment option for ND AML patients.
Reference
Dimopoulos M., et al. An all-oral regimen of decitabine-cedazuridine (DEC-C) plus venetoclax (VEN) in patients (pts) with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) ineligible for intensive induction chemotherapy: Results from a phase 2 cohort of 101 pts. JCO 43, 6504, (2025).
WaveLINE-003 Phase 2/3 Trial: Efficacy and Safety of Zilovertamab Vedotin (ZV) plus Standard of Care in R/R DLBCL
- The study showed ZV, in combination with R-GemOx, was effective and safe at a RP2D of 1.75 mg/kg as compared to ZV doses of 1.5 mg/kg or 2.0 mg/kg in R/R DLBCL.
- Almost all patients reported TRAE (AE, 98% patients) with grade ≥3 TRAEs reported in 65% patients; neutropenia, neutrophil count decreased, platelet count decreased, and anemia being the most common.
- However, discontinuations due to AE were low (n=2); 1 pt died due to sepsis in the 2.0 mg/kg dose cohort.
- ZV 1.75 mg/kg (56%) achieved an objective response rate similar to ZV 2.0 mg/kg (57%) and higher than ZV 1.5 mg/kg (27%).
- The median duration of response was 14.4 mo for ZV 1.5 mg/kg and 8.7 mo for ZV 1.75 mg/kg.
- ZV 1.75 mg/kg dose achieved a higher 6-month OS rate (78.8%) as compared to ZV 1.5 mg/kg (70.0%) and ZV 2.0 mg/kg (68.6%).
- ZV + R-GemOx demonstrated promising efficacy and acceptable safety in R/R DLBCL at the RP2D of ZV of 1.75 mg/kg.
Reference
Armand P., et al, WaveLINE-003: Phase 2/3 trial of zilovertamab vedotin plus standard of care in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. JCO 43, 7005, (2025).
The ADVANCE Clinical Trial: Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide, & Dexamethasone (KRd) with or without Daratumumab (D) in Patients with NDMM
- As per the 2nd prespecified analysis, treatment with DKRd KRd showed 2.5-fold higher MRD negativity at 10^-5 by NGS (59%. 36%, adjusted OR = 2.5, 95%CI: 1.5-4.2; P<0.0007)
- The current data on PFS & OS are data immature, PD 4 vs. 5%, & 86 vs. 79% remained progression-free & were censored in the DKRd vs KRd arms, respectively.
- Adverse events (AEs): hematologic AEs were reported in 15 vs. 24%; cardiac AEs: 13 vs. 16%; GI AEs: 68 vs. 72%; infections: 61 vs. 53%; AKI: 1 vs. 4%; vascular disorders: 6 vs. 2% in DKRd vs. KRd arm. The incidence of serious AEs was >1%.
- DKRd appears to be a promising new standard for most NDMM patients receiving initial KRd-backbone therapy.
Reference
Carl Landgren, et al. Randomized, multi-center study of carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd) with or without daratumumab (D) in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM): The ADVANCE clinical trial. JCO 43, 7503, (2025).